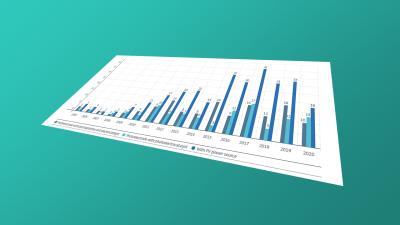
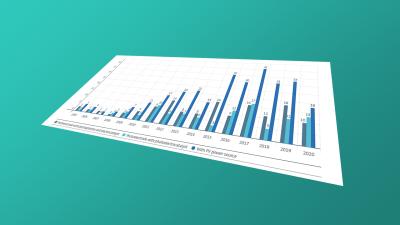
Protection beyond 20 years: data on SPCs and other term extensions for pharmaceutical patents
Developing new drugs is a long and complex procedure. Before bringing a new medical product to market, pharmaceutical companies need to conduct all kinds of studies, trials and safety tests to obtain marketing approval from the relevant government authority. On average, this process takes around 12 years, which significantly shortens the effective period of patent protection for a new product.
To compensate patent holders for this "loss", various patent authorities around the world have introduced patent term extension systems for IP rights in pharmaceutical fields, including Supplementary Protection Certificates (SPCs) in the European Union.
This series of articles takes an in-depth look at SPCs. After introducing their basic features, we show you how you to access data on SPCs and other forms of term extensions using the EPO's search tools. Finally, we also explore SPCs for patents with unitary effect.
To set the scene, we begin by comparing SPCs with term extension systems in other major jurisdictions.
Part I: Basic concepts at a glance
Background
Patent term extensions for drug patents were first introduced in the U.S. in 1984, with South Korea following suit in 1987 and Japan in 1988. The EU subsequently introduced SPCs in 1993, primarily to ensure that European pharmaceutical companies did not suffer any competitive disadvantage compared to their counterparts in other major jurisdictions.
Unlike regulations in the U.S., South Korea or Japan, SPCs are not term extensions by strict definition, but rather separate IP rights that come into effect once the related patent expires. The table below compares the key features of SPCs with those of patent term extensions (PTE) in other major jurisdictions.
Requirements
|
|
EU (SPCs) |
U.S. |
South Korea |
Japan |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Eligible technical fields |
Pharmaceuticals, Plant protection products |
Pharmaceuticals, Agrochemicals |
Pharmaceuticals, Agrochemicals |
Pharmaceuticals, Agrochemicals |
|
Eligible categories of patents |
Substance, process, use, composition |
Substance, process, use, composition |
Substance, process, use, composition |
Substance, process, use, composition |
Request
|
|
EU (SPCs) |
U.S. |
South Korea |
Japan |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Authority to grant extension/SPC |
|
U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) |
Korean Intellectual Property Office (KIPO) |
Japan Patent Office (JPO) |
|
Time period for filing request |
Within 6 months of either marketing approval or grant of the patent, whichever is later |
Within 60 days of marketing approval and prior to the expiry of the patent |
Within 3 months of marketing approval, but not later than 6 months from the end of the patent term |
Within 3 months of regulatory approval, but not later than 6 months from the end of the patent term |
|
Person eligible to file request |
Only patent owner (i.e. not licensee or other third parties) |
Only patent owner (i.e. not licensee or other third parties) |
Only patent owner (i.e. not licensee or other third parties) |
Only patent owner (i.e. not licensee or other third parties) |
Period of extension
|
|
EU (SPCs) |
U.S. |
South Korea |
Japan |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Maximum number of extensions per patent |
One |
One |
One |
Several*** |
|
Calculation of period of extension |
Period between filing date of patent and date of marketing approval, reduced by a period of 5 years |
Period consisting of half of the testing phase of the product and entirety of the approval phase by the government authority responsible |
Period between either patent grant or start of clinical tests (whichever is later) and marketing approval |
Period between either patent grant or start of clinical tests (whichever is later) and marketing approval |
|
Maximum period of extension |
5 years |
5 years |
5 years |
5 years |
|
Paediatric extension permitted? |
Yes (6 months)** |
Yes (6 months)** |
No |
No |
|
Maximum remaining term from product approval until end of extended term |
15 years |
14 years |
No limitation |
No limitation |
* Subject to approval of the unitary SPC by EU legislative bodies.
** The paediatric extension can be granted as further compensation for research and development of medicines for children. The maximum extension period may therefore cover 5.5 years.
*** Multiple extensions possible, e.g. for several active ingredients included in the same product or for several applications or dosages of the product. However, these extensions are not aggregated but run in parallel, i.e. the maximum period of extension is still limited to five years.
Preview:
Next issue of Patent Knowledge News: SPC bibliographic data and certificates in the EPO’s search tools.
Keywords: SPC, supplementary protection certificate, term extension, pharmaceutical, drug